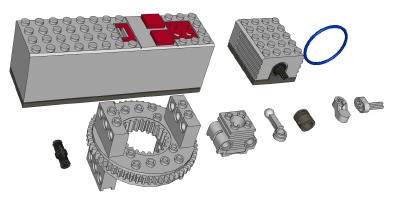
9V Electric
System
1990 saw the release of a brand new motor system.
The old 4.5V motor and battery box were replaced with new 9V versions.
- The new battery box held 6 AA (LR6) size batteries (1.5V)
in series and was 4x14 studs in area. There was a single
electrical output connection. A rocker switch controlled polarity
to run the motor either forwards of backwards. This is a very
sturdy motor box although if you ever get corrosion inside from the
batteries it will take you a very long time to rebuild it.
- The new 9V motor was 4x5 studs in area with a single axle
output. Typically a small toothed bushing was used as a pulley on
this output. This is a high speed motor which requires
significant gear reduction to be used for any useful function.
- A new blue belt was typically used as the main drive system
from the motor. Use of a belt allowed the motor to slip rather
than stall if too much torque was applied. Unlike the old rubber
bands, this belt was not made from rubber but some other type of
elastomer which does not degrade over time when installed under
tension. There was also a smaller white belt.
- The new electrical wires (not shown) used a 2x2 plate with
4 contacts. This connector was specifically designed to make sure
that it could never be shorted. The polarity of the motor could
be reversed by rotating the connector 90 degrees.
Modified Friction Pin
The new black friction pin looked very similar to the old. The
major difference is that a longitudinal slot was added which makes the
pin compress slightly when installed. This makes it much easier to remove than the old
variety. This part would become a staple of Technic construction
up to the present day. There are probably more of this part in
Technic sets than any other.
Turntable
A new turntable was introduced as a vast improvement over the old 4x4
circular variety. It was a large diameter and featured both an
internal (24 tooth) and external (56 tooth) ring gear so it could be
driven by gear systems
on the model. The internal ring gear was attached to the lower
half of the turntable, and the external ring gear to the upper.
The internal ring gear was the same size as a 24
tooth spur which fit perfectly inside. With 6 pin holes on the
top and the bottom, it
could support significant weight. It was used on many of the
larger sets for many years.
Engine
Elements
While the old reciprocating engines had a unique 2x2 piston part, the
rest of the engine was made with standard parts. That changed in
1990 with the introduction of a whole new engine system comprised of
parts designed to work together. This system would be used on a
wide variety of sets for decades.
- A 2x2 cylinder block featured a round bore and simulated
cooling fins on the exterior Two pin holes on either end were
used to mount it.
- A round piston fit snugly inside the bore of the cylinder
and had a spherical ball receptacle on the lower end.
- The connecting rod has a ball joint at the top and a hole
at the bottom. The rod was offset 1/2 stud width so that opposing
pistons could be aligned in the same plane, something which was not
possible with the old engines.
- A crankshaft end piece had an axle on one end and an axle
recess offset 1/2 stud on the other end. This allowed a
crankshaft to be constructed with a 1 stud stroke.
- A central crankshaft piece had an axle recess on either end
offset one stud with. It was used for engines with more than two
cylinders requiring a longer crankshaft.
Tire
A new 20x30 solid foam balloon tire was introduced which fit on the
existing 20x30 wheel.
|

|






